PROSTATE CANCER
In the last decade of the 20th century, the human population will increase by 1 billion, but in the next 25 years it will approach 2 billion. A person born in 1920 shared this world with 1.5 billion people and now shares it with 6 billion people. In our lives, a rapidly aging population (> 65 years old) and very old (> 85) populations are formed. As the elderly population triples, a 20-35% decline in the number of children is foreseen.
Incidence
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, while cancer is the second leading cause of death. (Figure 1)In the last 20 years, awareness about the disease has increased significantly, which has played an important role in early diagnosis.
Today, one out of six men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer. Prostate cancer has a very irregular distribution in terms of race. The highest mortality rate is in African Americans, and the disease is very common in the Caribbean and Africa. Contrary to this situation, the disease in Asia has the lowest incidence and mortality rate.
Etiology
Prostate cancer are seen twice if prostate cancer was diagnosed in first-degree relatives. If there are 3 prostate cancers in first relatives, the risk is 9 times higher. At least 100 loci related to Pca were detected in genomic studies. A high fat diet causes increased prostate cancer risk.
Conversely, taking soy products (isofloxoids, phytoestrogens, Bowman-Birk inhibitors) can decrease prostate cancer development and progression.
Pathology
Most of the prostate tumors are adenocarcinomas originating from the acinar glands. Most of them originate from the peripheral zone (PZ) of the prostate gland and 25% of the central and transitional zone (CZ). The Gleason grading system has emerged as a standard in prostate cancer grading terminology.
Sign and Symptoms
This disease has no specific primary finding or symptom. Although these findings usually occur for other reasons, the urinary tract may be accompanied by obstructive symptoms or hematuria. (Figure 2) Unfortunately, bone pain may be the first symptom, but it reflects a very late period of disease.
Localised
Prostate cancer
Tumor factors such as the patient's age, general performance status, Gleason score, baseline PSA value, and calculated tumor volume / staging should be considered. It is not easy to assess the positive effect of cure if the chance of 10-year survival is less than 50% because of other illnesses.
Active surveillance/watchful waiting
This approach is usually recommended for patients with comorbidities and/or fear of surgery. Patients who underwent surgical intervention for active surveillance have been shown to have advantages in terms of metastasis rate and disease-related life span in the last 8 years. These findings were more evident in patients under 65 years of age.
Radical
Prostatectomy
This is a suitable treatment choice for both young
patients and those who are elderly but enough fit for this treatment.
Generally, the chronological age is used as a relative limit of 70
years, but decisions must be individual. Surgical mortality is less
than 0.2%, but pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis may be seen
in 1-2% of patients.
Radiotherapy
RT is one of treatment options for localized prostate cancer and is the treatment of choice for T3 disease. All side effects can be reduced by adjusting dose intensity with important technical developments such as conformal radiation and intensity adjusted radiation therapy (IMRT). In general doses administered in divided doses of 70-80 Gy are well tolerated. Persistent rectal or bladder symptoms occur in approximately 3-5% of patients, and more than 60% of patients develop erectile dysfunction within 2 years.
Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma
Androgen ablation is the first choice in metastatic prostate cancer. This treatment can be done with gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, bilateral orchiectomy and finally with GnRH antagonists. Diethylstilbesterol (DES) is no longer used because it causes a high cardiovascular risk. Toxicity of androgen ablation includes hot flashes, loss of libido, impotence, musculoskeletal atrophy, and osteopenia / osteoporosis.
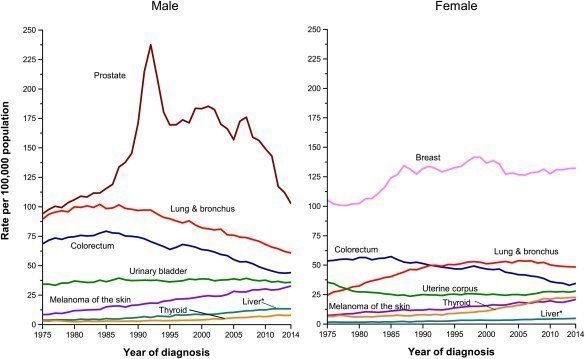
Figure
1: World Cancer Statistics
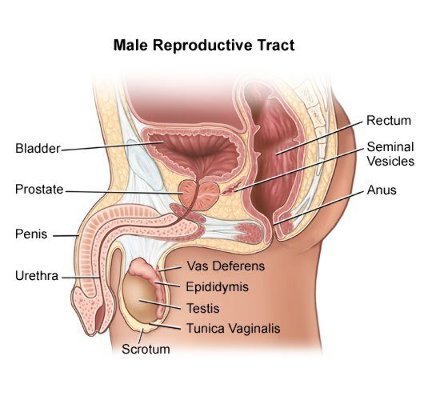
Figure
2: Anatomic relationship of the prostate gland.

 TOBB ETÜ HASTANESİ TIP FAKÜLTESİ
TOBB ETÜ HASTANESİ TIP FAKÜLTESİ
Loading...